Bidal, J.; Bil, A.; Destarkeet, V.; Hadad, C.; Nguyen Van Nhien, A.; Becuwe, M. R.
Here, we have synthesized and characterized a series of new hybrid materials based on ionic liquid grafted on metal oxide for designing solvent-free solid-state electrolytes. The aim of this study is to determine the key parameters affecting the ionic conduction properties of the materials. Several aspects were modulated, such as the chemical composition of the metal oxide (SiO2, ZrO2 or Al2O3), the anchoring bond (silane chemistry or coordinative bond) and the length and nature of the spacer (propyl, undecyl, polyethylene glycol). The ionic conductivity of the hybrid composite mixed with the lithium salt reach ionic conductivity of 4.10-5 S.cm-1 without any solvent or plasticizers. This study reveals that lithium mobility is affected by the molecular structure of the ionic liquid and the grafting function, but more driven by the organization of the ILs on the surface of the nanomaterial.
Dib, N.; Sauvage, F.; Quéhon, L.; Khaldi, K.; Bedrane, S.; Calvino, J. J.; Bachir, R.; Blanco, G. ; Pourceau, G.
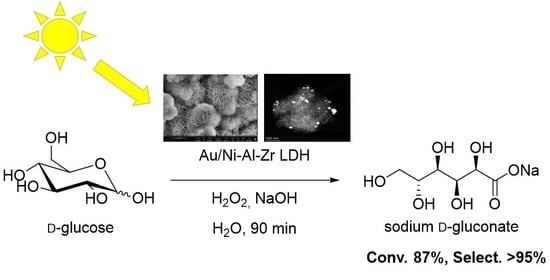
Confronting escalating challenges in energy security and environmental sustainability has intensified interest in renewable sources for fuels and chemicals. Among the most promising alternatives, sugars derived from biomass are emerging as a cornerstone in advancing an environmentally sustainable economy. Within this framework, the development of sunlight-driven carbohydrate oxidation is of significant interest, as it enables the production of a broad spectrum of high-value, bio-sourced chemicals through eco-friendly processes. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) immobilized on inorganic supports have demonstrated considerable potential in this area, although the methodology still requires further exploration. In this study, we explored the selective oxidation of glucose into the corresponding gluconic acid salt in presence of a novel Au/Ni-Al-Zr-layered double hydroxide (LDH) photocatalyst under standardized A.M. 1.5 G light illumination. To optimize the photocatalytic conditions, an experimental plan is herein proposed, highlighting the critical influences of both catalyst loading and pH. In optimal conditions, the Au catalyst demonstrated a high efficiency, achieving 87% glucose conversion and 100% selectivity towards gluconic acid in only 90 min. By means of long-pass filters to select the incident light energy to the photocatalytic reactor, we evidenced that the charge transfer processes were occurring from the Ni-Al-Zr LDH support to the gold nanoparticles, thus opening new directions towards further photocatalyst modifications. This work underlines the potential of Au/LDH materials for sunlight-driven photocatalysis and provides a pathway for the sustainable production of high-value chemicals from renewable biomass sources.
Singh, M.; Pourceau, G.; Quéhon, L.; Sauvage, F.; Banerjee, R.
Low-dimensional perovskites show great promise due to their stronger structural stability against external stressors, in particular, moisture. However, the alternance of organic and inorganic layers contributes to form a quantum-well structure leading to the bi-dimensional confinement of the carrier's transport, thus limiting the performances in solar-to-fuel conversion applications. To overcome this issue, the synthesis of the 1D vinylenedipyridine-based (4,4′-VDP)Pb2X6 perovskite (X = Br, I), whose specificity is to combine pi-conjugated spacer and cation–pi interactions, is reported. The pi-conjugation electronically connects the inorganic layers, and the cation–pi interactions facilitate stability against water. As a result, exceptional structural and photostability in a large range of aqueous pH is demonstrated. Whereas (4,4′-VDP)Pb2Br6 does not show photocatalytic activity toward hydrogen production due to misaligned band energy position with HBr, the iodide counterpart (4,4′-VDP)Pb2I6 perovskite produces a substantial amount of hydrogen (1.81 mmol g−1 after 24 h of photoreaction), without noble metal catalyst utilization and under standard AM 1.5 G illumination conditions.
Duarte-Serrano, D.; Waterlot, C.; Cézard, C.; Bouvier, B.; Barrientos, C.; Cuneo, I. F.; Fuentealba, C.; Hadad, C.; Nguyen Van Nhien, A.

The textile industry is a major driver of water pollution, releasing vast amounts of heavy metals, toxic dyes, and organic and inorganic contaminants, which severely harm the environment. Pollution remediation remains a major challenge, highlighting the need for efficient and cost-effective solutions. Biopolymer-based technologies provide a sustainable, efficient, and eco-friendly solution for industrial dye removal. Incorporating nanomaterials can enhance the adsorption capacity of these materials due to their high specific surface area. This study compares the effectiveness of nanomaterials such as cellulose nanocrystals (NCC), chitin nanocrystals (NCChit), and oxidized chitin nanocrystals (NCChit-ox). The results indicate that NCChit-ox is the most effective sorbent, exhibiting the highest Langmuir constant (KL) and a maximum adsorption capacity for methylene blue (MB) of 96.5 mg/g, with a removal efficiency exceeding 92.5% across all concentrations, as confirmed by molecular modeling. These nanomaterials were incorporated into bacterial alginate-based hydrogels for MB adsorption. The effects of temperature, contact time, pH, and dye concentration were studied. Among the evaluated isotherms, the adsorption experimental data best fit the Langmuir model (R² = 0.9547). Kinetic data suggest that the adsorption process follows a second-order mechanism (R² = 0.977). The hydrogel demonstrates excellent reusability, maintaining high adsorption efficiency across multiple cycles.
Duarte-Serrano, D.; Vallin, A.; Hadad, C.; Gonzalez Dominguez, J. M.; Cano, M. E.; Jamali, A.; Guénin, S.; Wadouachi, A; Nguyen Van Nhien, A.

Natural sulfated polysaccharides (NSP) are widely used in food, medical, and cosmetic applications. Chemical sulfation is typically required to mimic NSP properties, but it often involves toxic solvents, excess reagents, and long heating times. We report for the first time the sulfation of well-defined cellulose and (oxidized)-chitin nanomaterials by mechanochemistry using a sulfur trioxide–pyridine complex offering a greener alternative. In contrast to their unmodified counterparts, the sulfated compounds S-NanoCel, S-NanoChit, and SOsingle bondNanoChit exhibited significantly lower turbidity values of 25, 45, and 158 NTU, respectively, confirming their excellent water dispersibility. The presence of covalently bound sulfate groups was confirmed by FTIR spectroscopy with characteristic bands near 1250 and 820 cm⁻¹ and 13C NMR. Elemental analysis revealed degrees of substitution (DS) between 0.22 and 0.78, with S-NanoCel showing the highest DS. X-ray diffraction showed that the unmodified nanomaterials had crystallinity values ranging from 80 to 93 %. After sulfation, the crystallinity was reduced and is no longer quantifiable, although the overall crystalline structure remained visible, with lattice arrangements corresponding to the alignment of the polysaccharide chains. Finally, biological evaluation demonstrated that sulfated oxidized chitin exhibited the strongest heparanase inhibitory activity (IC₅₀ = 0.7 µg·mL⁻¹), suggesting its potential as a heparan sulfate analog.
Koffi Teki, D. S. E.; Coulibaly, B.; El-Abid, J.; Bil, A.; Vallin, A.; Kovensky, J.; Chagnault, V.

Heparan sulfate (HS) analogs are synthetic oligo- and polysaccharides designed to mimic or enhance several biological properties of native HS. Organic synthesized compounds are very useful tools for understanding the structure–activity relationships of many biological events. Unlike heterogeneous mixtures of tissue-isolated biomolecules, synthetic compounds offer a valuable platform to probe structure–activity relationships with reduced off-target effects in pharmacological applications. In our research group, we are particularly focused on the design and synthesis of thiodisaccharide analogs mimicking HS structural motifs. In recently published work, we reported the synthesis and biological evaluation of both new sulfated and non-sulfated O- and S-linked disaccharides, demonstrating their potential as heparanase inhibitors. In this article, we introduced a sulfonate moiety as a stable analog of the sulfate group. Comparative heparanase inhibition assays reveal that sulfated disaccharides exhibit significantly greater activity than their sulfonated counterparts. Furthermore, multivalent glycoclusters were prepared by coupling sulfated thiodisaccharides to maltotriose and cyclodextrin scaffolds, providing novel molecular architectures that show promising heparanase inhibition.
Desvals, A.; Lefebvre, C.; Martinez, A.; Hoffmann, N.

The cyclodextrin (CD) complexes of several butenyloxybenzonitriles were synthesized and irradiated as aqueous suspensions. An enantioselective intramolecular [2 + 2] or ortho photocycloaddition in such inclusion complexes is described. α-Cyclodextrin and β-cyclodextrin induce chirality in the opposite direction. At the reaction temperature (<7 °C), the enantiomeric excess (ee) is significantly increased (34% for α-CD, −10% for β-CD). The product yield in the cyclodextrin complex (35%) was close to that one of the racemic reaction in solution (42%). A topological analysis describes C2-symmetric chiral induction in a C6-symmetric host structure (α-Cyclodextrin). In a computational study, the energies of the inclusion complex were calculated for different conformations of compound 3a.
Racaniello, G. F.; Mathiron, D.; Rigaud, S.; Denora, N.; Leonetti, F.; Lopalco, A.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F.; Lopedota, A. A.

Direct printing of pharmaceutical powders allows the creation of personalized paediatric dosage forms, such as orodispersible films (ODFs). In this study, we present an optimized protocol to prepare midazolam (MDZ)/γ-cyclodextrin (γ-CD) inclusion complex-loaded ODFs using the innovative direct powder extrusion 3D printing technique (DPE). ODFs were formulated with a polymer blend consisting of polyethylene oxide and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, in the presence or without γ-CD. An in-depth analytical investigation using NMR and LC-MS spectrometry demonstrated that MDZ/γ-CD inclusion complex could form in situ during the printing process. ODFs with the preformed inclusion complex and MDZ alone were also prepared and characterized in terms of drug loading, morphology, disintegration, drug release, and mucoadhesion. ODFs containing either the in situ-formed or preformed inclusion complex were equivalent and exhibited superior performance compared to films without γ-CD. The use of γ-CD was particularly advantageous in enhancing the film disintegration and MDZ dissolution. MDZ-loaded ODFs were successfully developed using DPE to produce thin, fast-dissolving films that are particularly suitable for paediatric populations. This approach facilitated the production of personalized dosage forms suitable for emergency scenarios, including sedation, acute anxiety, and epilepsy and enabled the creation of beneficial molecular interactions that would typically require additional pharmaceutical processes.
Tinet, N.; Lesur, D.; Queneau, Y.; Soulère, L.; Djedaini-Pilard, F.; Bonnet, V.

In this work, acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) are grafted, the most studied signaling molecules in many Gram-negative bacteria, onto cyclodextrins (CDs) by copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition “click” coupling between alkynyl-AHLs and 6-azido-CDs derived from α- and β-CD, native or methylated. Attaching biomolecules onto a CD scaffold is a known strategy to enhance their properties, but designing CD-AHL conjugates has never been reported. These molecules were fully characterized by NMR and high-resolution mass spectrometry, and the study of their solubility and conformation reveals significant conformational changes due to the presence of the AHL appendage on the CD structure. One of the hybrids (per-AHL-β-CD, 9B) exhibits higher solubility in water than AHL and β-CD alone. The new CD-AHLs conjugates are found to modulate bioluminescence in a quorum Sensing LuxR-regulated light-producing bacterial model, with significant variations depending on the structure. The per-AHL-β-CD, 9B, is found to be the most active compound in the series.
Ishchenko, R.; Becuwe, M.; Dubois, L.; Gambarelli, S.; Cézard, C; Baudrin, E.

The development of aqueous organic redox-flow batteries (AORFB) requires finding new posolyte alternatives to the ferrocyanide salts used presently. Among the potential families, phenothiazine has been reported to be of interest if its solubility in aqueous medium is successfully increased. In this article, the phenothiazine propyl sulfonate (PTZPS) is evaluated as a promising high-potential posolyte for neutral-medium aqueous redox-flow battery. It is demonstrated that electrochemical reversibility is highly dependent on pH, with namely a fast capacity loss in neutral medium. Through the preparation of the oxidized form of this molecule, a kinetic study is performed, confirming the crucial role of the electron transfer step between two molecules at this redox state. Even if density functional theory (DFT) calculations of the electron transfer are not successful due to the significant multireference character of the oxidized form's dyad, using MD simulations, the behavior of the oxidized form in various media is qualitatively predicted, including the effect of addition of chaotropic additives.
H. Khartabil, A. Rajamani, C. Lefebvre, J. Pilmé, E. Hénon
The Electron Localization Function (ELF) has been successfully used to understand the concept of electron-pair localization in molecules and solids. The topological analysis of ELF enables partitioning of the molecular space into basins (core, valence, monosynaptic, and polysynaptic). The gradient field of ELF, examined using quantum chemical topology algorithms, is a key component of this analysis, which can be time-consuming. Combining ELF and the Independent Gradient Model (IGM), we propose a novel approach that is approximately two orders of magnitude faster than traditional methods, providing a rapid visual methodology to identify the synaptic order of ELF basins, which defines their connectivity and corresponding bonding schemes. We validate this combined approach across a wide range of representative chemical systems, demonstrating its efficiency in generating visual ELF analyses and in enhancing traditional approaches where topological analysis may struggle. The analysis serves as a stepping stone for full ELF topological analyses through programs like TopChem2.
Fortier, L.; Lefebvre, C.; Hoffmann, N.
Red-light-activated photocatalysis has become a powerful approach for achieving sustainable chemical transformations, combining high efficiency with energy-saving, mild conditions. By harnessing the deeper penetration and selectivity of red and near-infrared light, this method minimizes the side reactions typical of higher-energy sources, making it particularly suited for large-scale applications. Recent advances highlight the unique advantages of both metal-based and metal-free catalysts under red-light irradiation, broadening the range of possible reactions, from selective oxidations to complex polymerizations. In biological contexts, red-light photocatalysis enables innovative applications in phototherapy and controlled drug release, exploiting its tissue penetration and low cytotoxicity. Together, these developments underscore the versatility and impact of red-light photocatalysis, positioning it as a cornerstone of green organic chemistry with significant potential in synthetic and biomedical fields.
Hamdi, R.; Staccioni, I.; Gerber, J.; Rup-Jacques, S.; Hertzog, J.; Carré, V.; Sindt, M.; Lefebvre, C.; Boubaker, T.; Longevial, J.-F.

The study focuses on gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes. The research aims to synthesize a family of four mono- and four bis-gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes, each bearing a methacrylate motif, with yields ranging from 63% to 98%. Two model complexes from this series were tested toward sulfur-based nucleophilic attack to assess the possibility of a Michael addition to the acrylate motif, with a view to future bioconjugation. Experimental results reveal that thiolate addition occurs exclusively at the gold(I) center, regardless of whether the N-heterocyclic carbene is a mono- or a bis-carbene, leaving the acrylate motif untouched. This outcome is supported by theoretical calculations, which predict an activation energy of at least 4 kcal/mol favoring nucleophilic attack at the gold(I) center. These findings suggest that gold(I) NHC complexes could serve as effective "clickable" motifs in themselves, challenging the necessity of further functionalizing them with additional clickable groups for bioconjugation applications.
Kolender, A. A.; Pélingre, M.; Yacovone, C.; Przybylski, C.; Petit, E.; Koffi Teki, D. S. E.; Bonnet, V.; Kovensky, J.

Carbohydrate-derived polymers combine attractive features like abundant renewable resources, large stereochemical diversity and defined functionalization of the carbohydrates. Starting from β-cyclodextrin, a diazido heptasaccharide was regioselectively obtained in a few steps. It was used as a prepolymer for the A2B2 synthesis of alternating poly(glyco-triazole)s by copper assisted azido alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) with two dialkynes of different length and polarity, namely, 1,7-octadiyne and bispropargyl-polyetileneglycol-5. The resulting polymers were completely characterized by FTIR, NMR, MALDI-TOF-MS, SEC MALS, thermal analysis (TG and DSC), and SEM. The alternating insertion of the heptasaccharide and dialkyne in linear polymeric structures was confirmed by NMR and MALDI-TOF experiments. The water-soluble poly(glyco-triazole) containing PEG units had Mn 20,640 and Mw 39,650. The thermal properties (Tg = 27–42 °C) were close to those of amylose but were influenced by the linker. Therefore, these new poly(glyco-triazole)s could be considered as polysaccharide mimics and alternatives to modified native polysaccharides or brush polymers.
Koffi Teki, D. S. E.; Thankappan, H.; Pélingre, M.; Ndour, M.; Przybylski, C.; Petit, E.; Bernard, J.; Bonnet, V.; Drockenmuller, E.; Kovensky, J.

The synthesis of well-defined oligosaccharides via cyclodextrin (CD) ring opening is an efficient method for obtaining tailored monomers, which are then suitable for further polymerization. Starting from benzoylated β-CD, which contains seven glucose units, pure difunctionalized benzoylated heptaoses were synthesized. This approach produced heptaoligosaccharides with either azide (A) or propargyl (B) as reactive groups at the reducing and non-reducing ends with a yield between 81 and 96 %, and corresponding to α,ω-diazidoheptaose, α,ω-dipropargylheptaose, and ω-azido-α-propargylheptaose for the AA, BB, and AB monomers, respectively. A highly efficient deprotection process provided access to difunctionalized linear and polar heptasaccharides with high purity (87–99 %). The newly synthesized oligosaccharidic blocks were then polymerized via copper-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition leading to seven original and distinct polymers. These include unprotected (AA-BB or AB-AB) or benzoylated (AB-AB) homo- and hetero-copolymers, as well as hydrophobic blocks randomly distributed with hydrophilic ones (AB-AB) or alternating unprotected-benzoylated blocks (AA-BB). Two additional polymers were obtained by quaternization of triazole rings. Characterization by SEC, TGA, XRD, NMR, and MALDI-TOF MS revealed that a mixture of polymers containing 1–34 blocks could be obtained, with a degree of polymerization ranging from 126 to 238 sugar units and moderate to excellent yields (30–85 %).
Waterlot, C.; Duarte-Serrano, D.; Hadad, C.; Jamali, A.; Nguyen Van Nhien, A.
_

The present work presents the efficiency and the limit in using bionanosorbents (cellulose, chitin and modified chitin nanocrystals) for the sorption of metal ions M2+ (M = Ni and Cd) in batch systems. Bionanosorbents were extracted from plants and shrimp shells, two available and low-cost materials. If cellulose and chitin nanocrystals did not efficiently remove metals in the experimental conditions of this work, the surface-modified chitin exhibited enhancement for the Ni2+ and Cd2+ adsorption capacity than original chitin nanocrystals. The Langmuir and Freundlich models fitted well to the experimental data from which the maximum adsorption capacity was 139.2 mg Ni g−1 and 38.4 mg Cd g−1. Regarding the Gibbs free energy and the Hall parameter, the sorption of Ni2+ and Cd2+ were spontaneous and favourable for pH around the neutrality. This corroborates the examination of IR spectra of oxidized chitin nanocrystals before and after the sorption process from which the metal removal mechanism was mainly attributed to the formation of complexes and ion exchanges of the bionanosorbent and metal ions. Element mappings of the bionanosorbents after sorption revealed a homogeneous distribution of Cd(II).